Azure DevOps with Continuous Integration & Continuous Testing
- Ankush Madaan
- Blog
About

Industries
- Azure, CI/CD, Continuous Testing, DevOps, Microsoft
Share Via
Introduction
Azure DevOps is a Software as a Service (SaaS) based solutions offered by Microsoft that provides end-to-end solutions for businesses to integrate DevOps procedures during their software cycle. Azure DevOps offers a highly scalable environment for developing and deploying simple to sophisticated software on any language, cloud, or platform. Thus, making it ideal for businesses to leverage any single Azure DevOps Services or to match with high-scale project management and task management requirements
Though Azure DevOps started in October 2018, initial roots began as early as in 2006 with the launch of the ‘Visual Studio Team System’.
Services that define Azure DevOps
- Azure Boards: To connect with your teams for planning, discussing, and tracking activities across the organization.
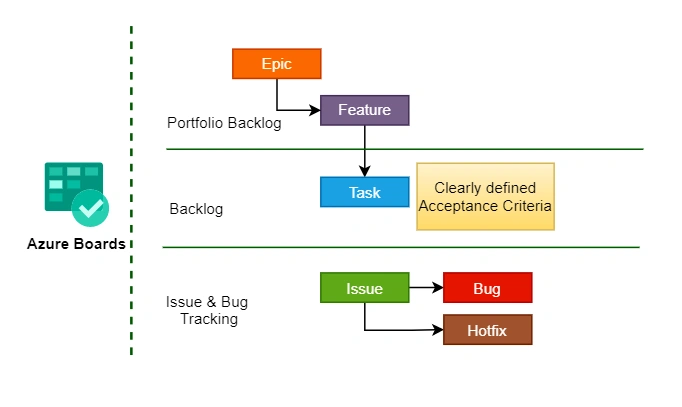
- Azure Pipelines: Enjoy working in a fully supported cloud-hosted pipeline for all platforms Windows, Linux, and macOS in developing, testing, and deploying applications more quickly and flexible with extensive support for the latest containers or Kubernetes.
- Azure Repos: Streamline automated workflows for a cloud-to-cloud integration for securing code in Git repositories throughout the software development cycle.
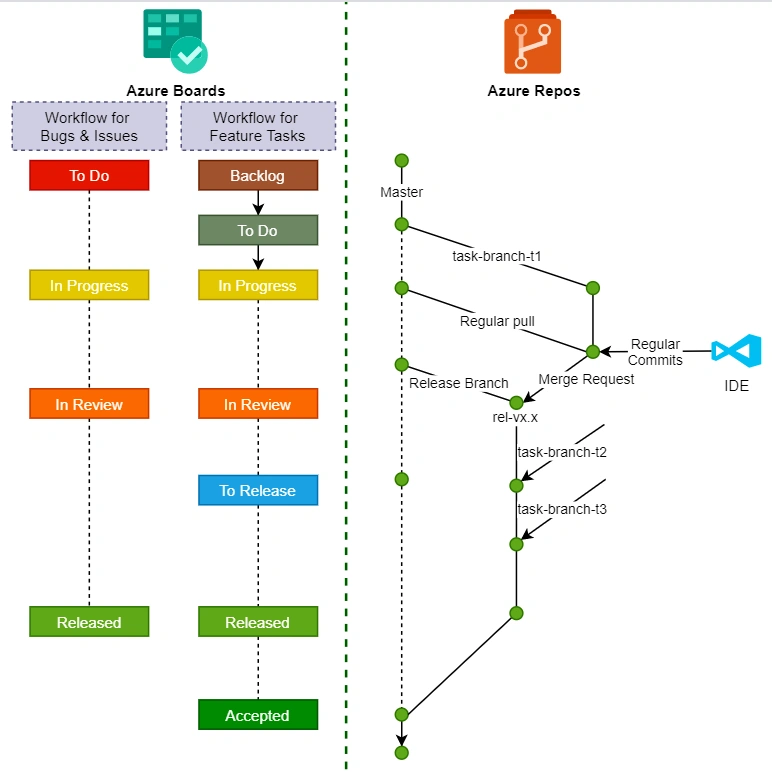
- Azure Artifacts: Seamlessly integrate CI/CD pipelines with your system architecture to share packages across teams.
- Azure Test Plans: Leverage the best manual and automatic testing tool in the IT industry to enhance your productivity.
You can also find thousands of other extensions to match your customized requirements supported by a large community.
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD)
One of the primary advantages of Azure DevOps is its extensible support through CI/CD tools. Businesses can seamlessly integrate with their existing tools to leverage the Azure Resource or even manage them via third-party tools such as Puppet, Chef, or Terraform to upgrade their software with Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD).
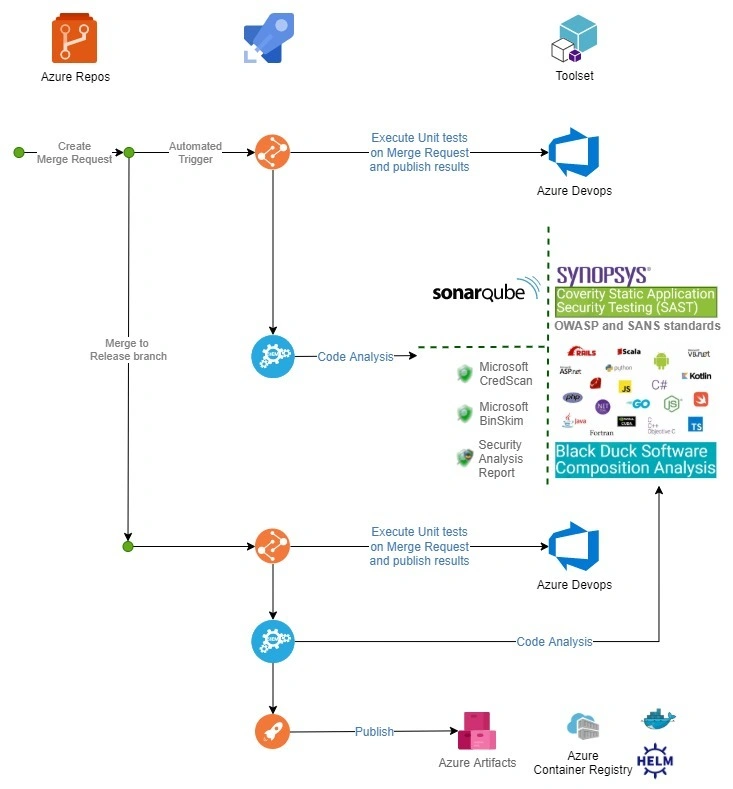
And with Continuous testing you can make sure to test all your codes before deploying and keep the product quality for delivering customer satisfaction at an optimum level.
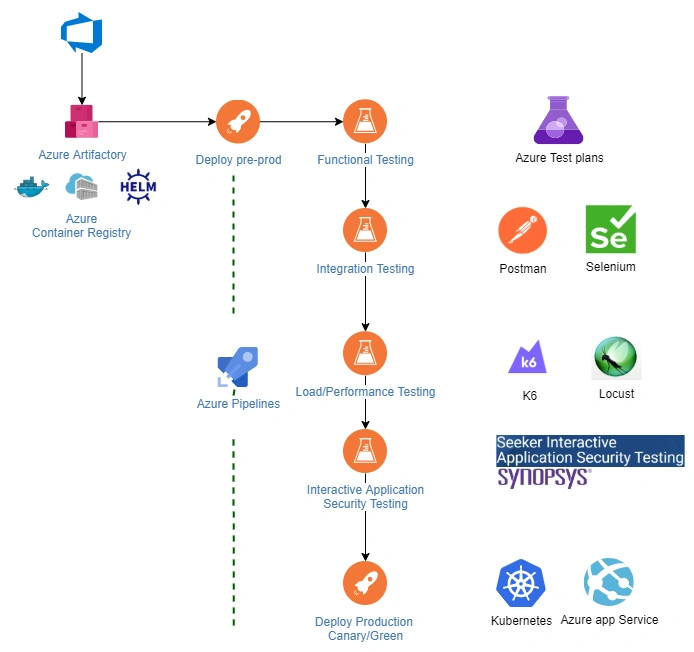
Azure DevOps Benefits
- Trusted and Reliable: Today, Microsoft Azure DevOps solutions are among the most trusted solutions for businesses with 24×7 customized support, 99.9% uptime, and enterprise-level security.
- Impeccable Integration: With Azure DevOps, you can connect with any app, 3rd party tools, platform, or any complex architecture to leverage particular gains.
Qualities that Make Azure DevOps the Best in the Industry
Flexibility: You can work with any services of the Azure DevOps tools to match your business requirements and get customized support.
Platform Independent: Azure is ideally suited for operating systems (Windows, Linux, or macOS) and with all language support for Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, C/C++, iOS, Android, and Node.js applications.
Cloud Independent: Azure DevOps is an entirely independent tool and even integrates effortlessly with other cloud providers such as Google Cloud Platform or Amazon Web Services.
Packed with more than 600 services, Microsoft Azure DevOps has become one of the preferable choices for businesses to get sophisticated solutions to stay ahead in this modern competitive market.
Frequently asked questions
Azure DevOps is a set of development tools and services, including Azure Pipelines, which enable automated Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Testing, and Continuous Deployment (CD) to streamline and speed up software delivery.
Go to Azure Pipelines, create a new pipeline, and configure it with a YAML file or a visual editor to define stages like build and test. Specify the trigger to run the pipeline on code pushes or pull requests.
CI automates code integration by testing every code change immediately after it’s pushed, catching issues early, reducing integration risks, and enabling a faster feedback loop for developers.
Add a test step in your Azure Pipeline to run unit tests using testing frameworks like MSTest, NUnit, or xUnit. Configure this to run after the build stage so that only successful builds move to the testing stage.
You can integrate UI testing tools like Selenium or Playwright in your pipeline. Create a separate test stage for UI tests to ensure they run only after passing unit and integration tests.
Set up automated test jobs in the pipeline to run at different stages (unit, integration, end-to-end) whenever code changes are pushed, so each code change is validated for quality before deployment.
Use the Publish Test Results task in your pipeline to collect and publish results from test runs. Azure DevOps provides a test summary view with detailed reports on test success, failures, and coverage.
Use tools like SonarQube or CodeQL to analyze code quality. Add them as tasks in your pipeline, configured to run after the build or test stages, ensuring code meets quality standards before merging.
Set up a CD pipeline in Azure DevOps to trigger deployment after successful tests. You can configure multiple deployment stages, such as staging and production, with approvals to control each step.
Use parallel jobs for faster builds, configure pipeline caching to reduce download times, and optimize test suites by focusing on essential tests. Azure DevOps also allows pipeline agents to run tasks concurrently, improving pipeline efficiency.
Related Posts

Comprehensive Guide to HTTP Errors in DevOps: Causes, Scenarios, and Troubleshooting Steps
- Blog

Trivy: The Ultimate Open-Source Tool for Container Vulnerability Scanning and SBOM Generation
- Blog

Prometheus and Grafana Explained: Monitoring and Visualizing Kubernetes Metrics Like a Pro
- Blog

CI/CD Pipeline Failures Explained: Key Debugging Techniques to Resolve Build and Deployment Issues
- Blog

DevSecOps in Action: A Complete Guide to Secure CI/CD Workflows
- Blog

AWS WAF Explained: Protect Your APIs with Smart Rate Limiting
- Blog

