Cloud Security and Compliance - Amazon Web Services
The era of cloud computing has become crucial for modern enterprises. Ensuring data protection, therefore, is not optional in neither product nor backend infrastructure in light of the growing number of cyber threats and changing regulations. Over 30% of surveyed organizations reported a cybersecurity threat almost every week. This number only becomes more concerning when cloud operations are involved.
AWS’ cloud security and compliance enter the picture here, providing tools and frameworks to protect crucial data from cyber threats and ensure regulatory alignment.
In this blog, you’ll read about how AWS cloud security basics such as automated monitoring, identity management, and encryption approaches help support cloud protection every step of the way.
Understanding Cloud Security and Compliance
As we mentioned above, security and compliance in cloud environments are absolutely crucial for all businesses using the cloud, particularly on such a large platform as AWS. Let’s take a look at some of the fundamentals of cloud security now.
Cloud Security Fundamentals
Cloud security requires a dynamic approach to address unique challenges, such as:
- Shared Responsibility: Cloud providers share security responsibilities with users. While providers secure the underlying infrastructure, users are responsible for securing their data, applications, and operating systems.
- Scalability: Cloud environments can rapidly scale up or down, necessitating flexible and adaptive security measures.
- Data Dispersion: Data can be distributed across various services and geographic locations, making it essential to implement robust access controls and encryption.
- Automation: Cloud security heavily relies on automation for real-time monitoring, threat detection, and incident response.
Traditional Security vs. Cloud Security
Traditional and cloud security approaches diverge significantly. While traditional security relies heavily on physical measures, cloud security is predominantly policy-driven and managed virtually. A few key distinctions include:
- Control Paradigm:
- Traditional: Companies maintain full control over on-premises infrastructure.
- Cloud: Control is shared between the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer.
- Traditional: Companies maintain full control over on-premises infrastructure.
- Adaptability:
- Traditional: Static environments are easier to secure, as security measures can be consistently applied.
- Cloud: Dynamic and ever-changing infrastructure requires a more adaptable security approach.
- Traditional: Static environments are easier to secure, as security measures can be consistently applied.
Next, let’s talk about how AWS cloud security is achieved through one of Amazon’s fundamental security models.
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model is a fundamental concept in Amazon’s cloud security services, outlining the division of security responsibilities between Amazon Web Services (AWS) and its customers. This model ensures a collaborative approach to security, where both parties play a vital role in protecting data and applications.
Key components of the Shared Responsibility Model include:
- AWS's Responsibility:
- Physical and Operational Security: AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud, including the physical security of data centers, network infrastructure, and hardware.
- Infrastructure Security: AWS ensures the security of the infrastructure, such as operating systems, hypervisors, and networking components.
- Regular Security Patches: AWS applies regular security patches and updates to its infrastructure to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Physical and Operational Security: AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud, including the physical security of data centers, network infrastructure, and hardware.
- Customer's Responsibility:
- Customer Data: Customers are responsible for securing their data, including encryption, access controls, and data protection measures.
- Guest Operating Systems: Customers are responsible for securing the guest operating systems, applications, and data running on AWS infrastructure.
- Network Configuration: Customers are responsible for configuring network security groups and security groups to protect their resources.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Customers must implement strong IAM policies to control access to their AWS resources.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Customers must comply with data protection regulations and ensure data privacy.
- Customer Data: Customers are responsible for securing their data, including encryption, access controls, and data protection measures.
Now that you have an idea of how the security model works, let’s take a look at the key challenges that AWS cloud security was designed to address.
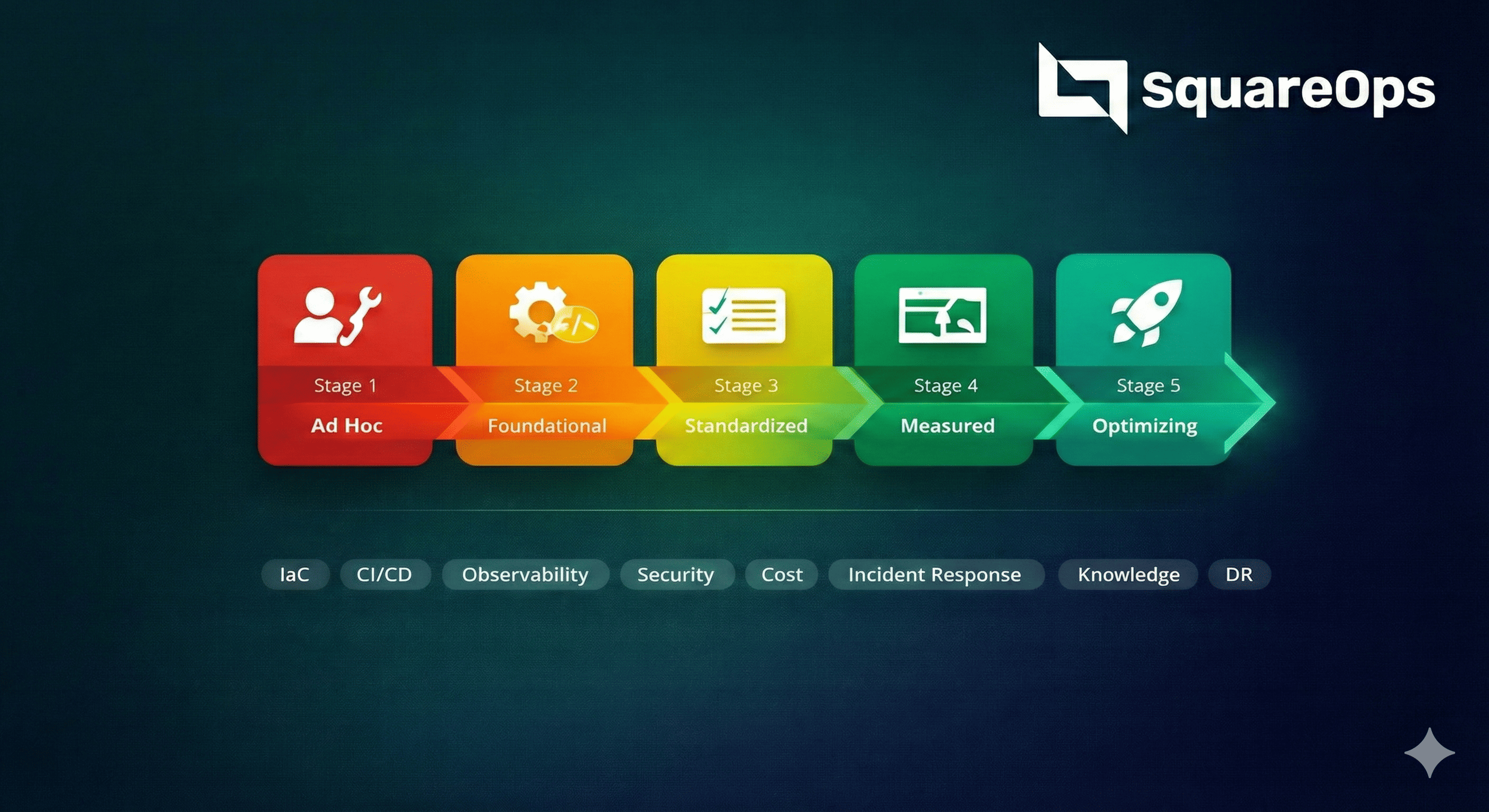
Key Security and Compliance Challenges in AWS

Security is never simple when working on AWS. The speed of change in the cloud, multi-cloud configurations, and compliance requirements make proper data protection more important than ever.
Let’s learn about these challenges and understand the various practices for mitigating these challenges, which we’ve listed below:
- Monitoring For Threats: It’s critical to be able to detect potential cloud security threats and vulnerabilities in a timely manner, or else your entire cloud infrastructure can be compromised. SIEM is a security solution that helps organizations recognize and address potential security threats and vulnerabilities before they can disrupt business operations.
- Implementing Access Control: It’s essential to control the availability of resources to avoid excess compute usage, which can lead to extra billing. Businesses can control usage permissions and reduce risk to crucial resources as part of this, using services like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Monitoring and Logging: Tracking and analyzing user activity and system events to identify suspicious behavior can be challenging, especially in dynamic cloud environments. This is where you can use utilities like Amazon CloudWatch or the AWS APIs. Both of these allow you to track actions over time — specifically with fields pertaining to API call history in Amazon CloudTrail.
- Data Protection Through Encryption: Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data both at rest and in transit is crucial, but it can be difficult to implement and maintain strong security controls. Here, you can employ strong encryption mechanisms, such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS), to encrypt data and use secure communication protocols like HTTPS to protect data in transit.
- Putting a Compliance Framework in Place: Compliance frameworks enable standardization of security across cloud environments. This allows you to map your AWS architecture with compliance standards such as ISO 27001 or HIPAA, enabling you to comply legally.
- Developing a Concise Incident Response Plan: A well-thought-out response plan will allow for swift responses to security incidents. AWS also offers services and features such as AWS Config to help you detect unexpected changes so that the blast radius of a change can be minimized.
- Integrating Threat Intelligence Operations: Services like AWS GuardDuty threat intelligence interrogate the network traffic and activity logs to raise the alarm in case of any anomaly. It helps organizations detect threats ahead of time.
As robust as these measures are, they can be daunting. SquareOps provides expert consultation and personalized security services for organizations that need to secure their cloud environments.
Learn more about how SquareOps can improve your AWS Cloud Migration.
AWS Security and Compliance Best Practices
AWS security best practices are a set of configuration guidelines that help build an array of defenses to establish the baseline for securely hosting workloads on AWS.
- Adopt A Shared Responsibility Model: Understand the division of security responsibilities between AWS and the customer. AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud, while customers are responsible for security in the cloud.
- Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM): Use strong IAM policies to control access to AWS resources, using the principle of least privilege.
- Ensure Data Encryption: Encrypt data both at rest and in transit using AWS KMS and TLS to protect sensitive information.
- Adopt Good Network Security: Configure security groups and network ACLs to control inbound and outbound traffic. Use VPN or Direct Connect to securely connect on-premises networks to AWS.
- Enable Monitoring and Logging: Use CloudWatch to monitor system health, application performance, and security events. CloudTrail logs user activity and API calls to track security incidents.
- Implement Incident Response Plan: Develop and test a comprehensive incident response plan to respond effectively to security incidents.
- Conduct Regular Security Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments, including vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
- Adhere To Compliance Framework: Adhere to relevant compliance frameworks like CIS, which is a global set of benchmarks that include HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS.
- Ensure Configuration Management: Use AWS Config to monitor and enforce configuration standards.
- Use Security Groups and Network ACLs: Use security groups and network ACLs to control inbound and outbound traffic.
A Partner For AWS Cloud Security
Ensuring cloud security and compliance is essential for any organization relying on AWS for cloud services. Mastering the basics of cloud security, in tandem with AWS’s advanced security tools, combines to form an extensive shield against threads.
SquareOps has vast expertise in AWS and the cloud business and offers competitive cloud security services. Organizations that want to improve their operations can rely on their team to develop tailored solutions matching their security profiles. We are also AWS-partnered and CIS-benchmark certified, giving us the edge to enable safe operations over 100 benchmarks across industries.
SquareOps can help you with everything from setting up to implementing and maintaining automation or operations within the DevOps ecosystem.