Simplify cloud access with AWS IAM Identity Center. Centralize user permissions, enable SSO, and integrate with apps and directories for secure, seamless management.
AWS WAF Explained: Protect Your APIs with Smart Rate Limiting
- Nitin Yadav
- Blog
About

Industries
- AWS, Cloud Security, Security, SquareOps
Share Via
Introduction
Keeping our web applications safe from unwanted visitors has become a non-negotiable part of running anything online. From data breaches to app slowdowns or full-on crashes, the risks are real—and they’re growing. That’s why having a Web Application Firewall (WAF) is no longer just an option; it’s a smart step forward. AWS WAF, or Amazon Web Services Web Application Firewall, is a tool designed to help us filter out the bad traffic while keeping the good stuff flowing.
AWS WAF is a cloud-native web application firewall that helps protect web applications from common threats and vulnerabilities. It works by filtering, monitoring, and blocking malicious HTTP and HTTPS traffic before it reaches our application. AWS WAF allows us to define custom security rules to block or allow requests based on various factors like IP addresses, HTTP headers, URI paths, and more. Unlike traditional firewalls that focus on network traffic, AWS WAF is tailored for web application security. It’s especially designed to protect against threats like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), etc.
Key Benefits of AWS WAF for Web Applications
- Scalability and Flexibility: Since AWS WAF is built into AWS services like Amazon CloudFront, AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB), and Amazon API Gateway, it can scale effortlessly with the application. Whether the application is handling a few requests per minute or millions, AWS WAF adjusts to meet our needs without requiring manual intervention. The flexibility allows us to tailor security policies to match the exact business requirements.
- Customizable Rule Sets: One of the standout features of AWS WAF is its customization capabilities. We can create custom security rules based on the specifics of our application. Whether it’s blocking traffic from certain geographic locations, restricting access to specific IPs, or preventing certain query strings in the URL, AWS WAF lets us fine-tune security policies to match our needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AWS WAF is a pay-as-you-go service, meaning we only pay for what we use. We are charged based on the number of rules created and the number of requests the application processed. This makes it an economical choice, especially for businesses that need scalable security without a huge upfront investment.
- Real-Time Visibility and Monitoring: AWS WAF integrates easily with Amazon CloudWatch, enabling us to monitor web traffic in real-time. We can track blocked requests, see attack patterns, and adjust our security policies accordingly. This visibility ensures that we are always aware of potential threats and can act quickly to mitigate them.
- Managed Rules: AWS offers pre-configured, managed rule sets that automatically protect our application from common threats. These rules are continuously updated to address emerging security risks, ensuring that our web application is always protected against the latest vulnerabilities without manual intervention. This feature can save significant time and effort for security teams.
How AWS WAF Works
AWS WAF works by inspecting incoming web traffic to the application before it reaches the server.
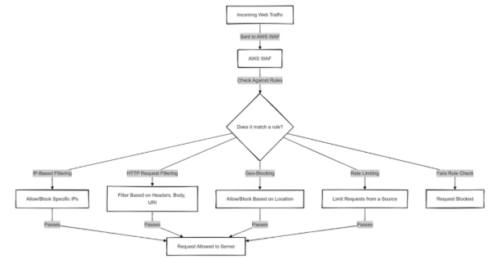
It uses rules that we define to determine whether to allow or block specific requests based on certain criteria. These rules can be tailored to our application’s needs and may include:
- IP-based filtering: Allowing or blocking specific IPs or IP ranges.
- HTTP request characteristics: Filtering traffic based on HTTP headers, body, or URIs.
- Geography: Restricting access based on the geographic location of the request.
- Rate-based filtering: Limiting the number of requests from a specific source in a given period.
Best Practices for Implementing Rate-Based Rules
Understand API Traffic Patterns
Before diving into rate limits setup, we should take a moment to examine the usual traffic patterns of our APIs. We need to look at metrics such as request volume, peak usage times, and how users typically interact with our service to create a solid baseline for our rate-based rules. AWS CloudWatch can help here to keep an eye on these metrics and visualize them effectively.
Set Meaningful Rate Limits
When setting a rate limit, it’s important to strike a balance between keeping the system safe and ensuring it’s user-friendly. If the limit is too strict, we might accidentally block genuine users. On the other hand, if it’s too relaxed, our APIs could be at risk of being misused. It’s a good idea to experiment with various thresholds in a staging (non-prod) environment to discover what works best for our application.
Combine with IP Sets
We can use AWS WAF IP sets for whitelisting trusted IPs or blocking those that are known to be malicious. This way, we can manage exceptions smoothly while still applying rate-based rules to the genuine application traffic.
Monitor and Adjust
We should keep an eye on blocked requests and tweak our rate limits whenever necessary. Review AWS CloudWatch logs to find patterns and fine-tune our rules to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Integrate with Lambda for Dynamic Responses
In case of some suitable use cases, we can integrate AWS WAF with Lambda functions to dynamically update IP sets based on real-time analysis. For example, we could automatically block IPs flagged as suspicious. And we can also integrate manual IP blocking functionality in the application itself, which will call AWS API and perform the IPSet update action to block or unblock specific suspicious IPs. This way, when a developer wants to block any customer IP, this can be done through the application itself by the developer, without DevOps intervention.
Protect Against Known Attack Vectors
We should implement rate-based rules alongside other WAF features like SQL injection and cross-site scripting protection. This will provide comprehensive API security to our application.
Steps to setup AWS WAF rate-limit rule
Step 1: Define a Regex Pattern Set
First, define a regex pattern set to match the specific URL paths we want to rate limit. In this example, we’ll limit requests to URLs starting with /api/v1/resources/.
- Navigate to the AWS WAF console.
- Go to Regex Pattern Sets and create a new regex pattern set.
- Add the following regex pattern to match the desired URL path:
Step 2: Create a Web ACL with a Rate-Based Rule
Next, create a Web ACL and add a rate-based rule that references the regex pattern set.
- Go to Web ACLs in the AWS WAF console and create a new Web ACL.
- Add a rule with the following configuration:
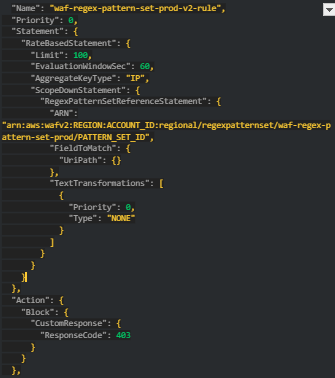

- Replace REGION, ACCOUNT_ID, and PATTERN_SET_ID with our respective AWS region, account ID, and pattern set ID.
Step 3: Associate the Web ACL with our Resource
Associate the Web ACL with our application resource (e.g., ALB or API Gateway).
- In the AWS WAF console, go to Web ACLs.
- Select our Web ACL and go to Associations.
- Choose the resource we want to protect and associate the Web ACL with it.
Step 4: Monitor and Test
To ensure our rate limiting rule is working as expected, monitor CloudWatch metrics and logs.
- Go to CloudWatch in the AWS Management Console.
- Check the metrics for the rule named waf-regex-pattern-set-prod-v2-rule.
- Enable logging for the Web ACL to capture detailed request logs.
Debugging Common Issues
If the rate limiting rule is not working as expected, consider the following steps:
- Verify Regex Pattern: Ensure that the regex pattern correctly matches the intended URL path. Use an online regex tester with sample URLs to confirm the match.
- Check Rule Configuration: Review the rule configuration in the AWS WAF console. Ensure the rate limit and evaluation window are set correctly.
- Monitor CloudWatch Metrics: Check CloudWatch metrics to see if the rule is being triggered. Look for any anomalies or issues in the metrics.
- Review WAF Logs: Enable and review WAF logs to see detailed logs of the requests being evaluated against the rules.
Adjust Limits: Temporarily reduce the rate limit to a lower value to see if it triggers more easily during testing.
Conclusion
Implementing rate limiting for specific URLs using AWS WAFv2 helps protect our application from excessive requests and potential abuse. By following the steps outlined in this blog, we can set up effective rate limiting rules tailored to our application’s needs. We need to monitor and adjust the configurations as needed to ensure optimal performance and security. By staying vigilant and proactive, we can safeguard our web application and provide a better user experience.
Frequently asked questions
What is AWS WAF used for?
AWS WAF protects web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP/HTTPS requests. It helps block malicious traffic such as SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS), ensuring only legitimate requests reach your application
How does AWS WAF rate limiting work?
AWS WAF uses rate-based rules to limit the number of requests from a specific IP address over a defined time. If the threshold is exceeded, WAF blocks further requests, protecting your API from abuse or denial-of-service attacks.
What are the benefits of using AWS WAF?
AWS WAF offers scalability, real-time monitoring, custom rules, managed rule sets, and seamless integration with AWS services like CloudFront and API Gateway. It enhances application security while being cost-effective and easy to configure.
How do I implement rate limiting in AWS WAF?
To implement rate limiting, define a regex pattern for your API URL, create a rate-based rule in a Web ACL, and associate it with your resource. Then monitor with CloudWatch to fine-tune thresholds and behavior.
Can AWS WAF block specific IP addresses?
Yes, AWS WAF can block individual IPs or ranges using IP sets. You can combine these IP sets with custom rules or rate-based conditions to restrict or allow traffic from selected sources.
How does AWS WAF help prevent DDoS attacks?
AWS WAF mitigates DDoS attacks by detecting traffic spikes and blocking malicious or excessive requests. With rate-based rules and integration with AWS Shield, it offers layered protection for web applications.
What is the difference between AWS WAF and a traditional firewall?
Traditional firewalls control network-level traffic, while AWS WAF secures application-layer traffic (HTTP/HTTPS). WAF offers fine-grained control over web requests, targeting web-based threats like injection attacks and bots.
How do managed rule groups in AWS WAF work?
Managed rule groups are pre-configured security rules provided by AWS or partners. They are continuously updated to protect against known threats, simplifying setup while ensuring up-to-date protection for your web apps
Can AWS WAF be used with API Gateway?
Yes, AWS WAF integrates directly with API Gateway. You can apply Web ACLs with custom or rate-based rules to protect your APIs from abuse, misuse, or malicious activity at the application layer.
How can I monitor AWS WAF performance?
Use Amazon CloudWatch to track AWS WAF metrics and logs in real-time. You can monitor blocked requests, request patterns, and rule effectiveness to optimize and adapt your security configurations as needed.
Related Posts

Comprehensive Guide to HTTP Errors in DevOps: Causes, Scenarios, and Troubleshooting Steps
- Blog
Comprehensive guide for DevOps on HTTP errors: causes, scenarios, and troubleshooting tips, covering status codes, SSL issues, CORS, timeouts, and server misconfigurations.

Trivy: The Ultimate Open-Source Tool for Container Vulnerability Scanning and SBOM Generation
- Blog
Explore Trivy: a fast, open-source tool for container vulnerability scanning and SBOM generation. Learn how it secures DevOps pipelines with ease and transparency.

Prometheus and Grafana Explained: Monitoring and Visualizing Kubernetes Metrics Like a Pro
- Blog
Set up Prometheus and Grafana for real-time monitoring and visualization in Kubernetes environments. Learn step-by-step configuration and best practices for DevOps success.

CI/CD Pipeline Failures Explained: Key Debugging Techniques to Resolve Build and Deployment Issues
- Blog
Learn how to identify and fix CI/CD pipeline failures—from environment mismatches to flaky tests—with practical solutions for reliable, efficient DevOps workflows.

DevSecOps in Action: A Complete Guide to Secure CI/CD Workflows
- Blog
DevSecOps integrates security into CI/CD pipelines, enabling early threat detection, compliance, and resilient infrastructure through automated security practices.

AWS WAF Explained: Protect Your APIs with Smart Rate Limiting
- Blog
AWS WAF protects web apps by filtering malicious traffic, blocking threats like SQL injection & XSS, and enabling custom rules, rate limits, and real-time monitoring.

