What is Cloud-Native Architectures?
Cloud-native architectures are designed to fully exploit the benefits of the cloud by leveraging microservices, containers, and serverless computing. These systems are built with scalability, resilience, and flexibility in mind, allowing applications to run efficiently across multiple cloud environments.
By adopting cloud-native architectures, businesses can innovate faster and scale seamlessly, adapting to growing demands with ease. This empowers companies to optimize resources, improve performance, and ensure a high level of fault tolerance, ultimately driving business agility.
Benefits of Cloud-Native Architectures
Faster Deployments
Automate manual processes to reduce time-to-market and deliver new features faster.
Scalability on Demand
Scale applications quickly to handle changing workloads and growing business needs.
Fault Tolerance
Ensure continuous availability and system resilience with self-healing architectures.
Cost Efficiency
Optimize resource usage with dynamic scaling to minimize costs while maintaining performance.
Enhanced Security
Implement security best practices at every layer, ensuring a secure environment from development to production.
Flexibility
Run applications seamlessly across hybrid or multi-cloud environments, maximizing infrastructure efficiency.
Cloud-Native Use Cases
Cloud-native architectures power a wide range of modern applications and scenarios, enabling businesses to innovate faster and scale seamlessly.
Dynamic Scaling
Automatically scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during traffic spikes.
Disaster Recovery
Build resilient systems with automated failover and geo-redundancy for business continuity.
Real-Time Analytics
Process and analyze streaming data in real-time for immediate insights and decision-making.
Continuous Deployment
Ship features faster with automated CI/CD pipelines and zero-downtime deployments.
Geo-Redundancy
Deploy applications across multiple regions for low latency and high availability worldwide.
Edge Computing
Process data closer to users at the edge for reduced latency and improved user experience.
Top Challenges We Solve
Monolith Limits Agility
Tightly coupled releases slow teams down and make scaling expensive and risky.
Our Solution
Domain-driven decomposition and microservices patterns with clear ownership and boundaries.
Inconsistent Environments
Environment drift creates “works on my machine” issues and deployment failures.
Our Solution
Containers + IaC + GitOps for repeatable builds, deployments, and governance.
Resilience & Cost Tradeoffs
Scaling without guardrails leads to outages, surprise bills, and unclear performance bottlenecks.
Our Solution
Well-architected patterns, autoscaling, observability, and FinOps-driven right-sizing.
Cloud-Native Architecture Patterns
Core patterns that make cloud-native platforms scalable, resilient, and easier to evolve.
We implement proven architecture patterns tailored to your business needs—from event-driven systems to multi-tenant SaaS platforms.
Event-Driven Architecture
Async messaging, pub/sub patterns, and resilient processing with retries & DLQs for real-time integrations.
Microservices
Domain-driven decomposition with clear boundaries, independent CI/CD, and better fault isolation.
Containers & Serverless
Portable deployments with Docker/Kubernetes and serverless functions for pay-per-use efficiency.
Distributed Systems
Multi-region resilience, traffic shaping, and failover planning for global-scale applications.
Multi-Tenant SaaS
Tenant isolation, data partitioning, metering, and guardrails for efficient multi-customer platforms.
Build Cloud-Native the Right Way
Modernize your platform with proven architectures, automation, and reliability-first practices.
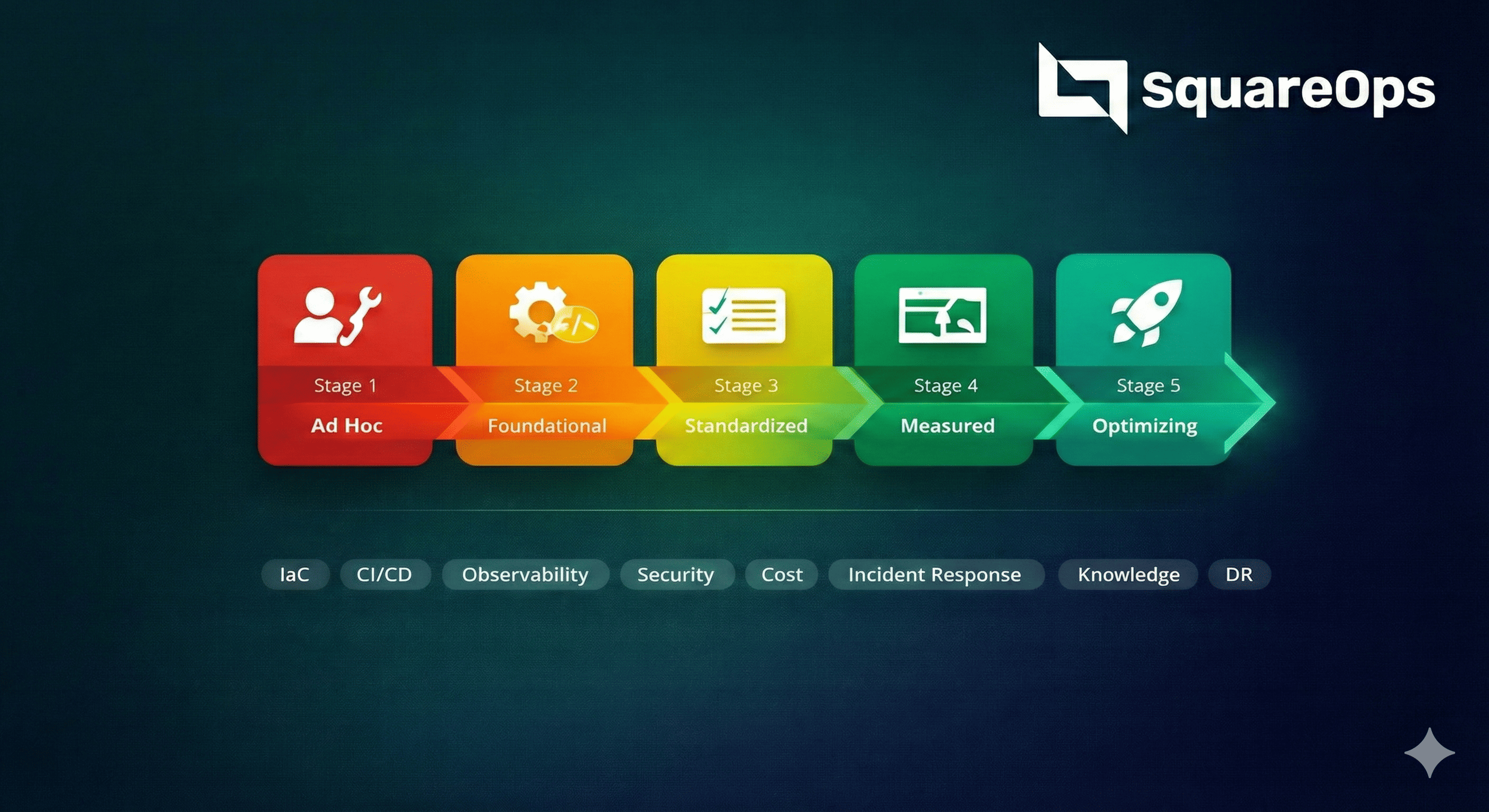
Get StartedCloud-Native Transformation: Your Implementation Journey
Our structured approach ensures a smooth transition from monolithic to cloud-native architecture.
Architecture Assessment
Analyze current architecture, identify modernization opportunities, and define target state with microservices boundaries.
Platform Foundation
Set up container orchestration, CI/CD pipelines, GitOps workflows, and infrastructure-as-code foundations.
Service Decomposition
Incrementally extract services from monolith, establish APIs, and implement service mesh for communication.
Observability & Security
Implement distributed tracing, metrics, logging, and security policies with policy-as-code enforcement.
Operational Excellence
Establish SLOs, runbooks, incident response, and continuous optimization for day-2 operations.